Introduction to Red Hat OpenShift Data Science
| This section is under development. |
Objective
-
Become familiar with the general architecture and main features of Red Hat OpenShift Data Science
The Complexity of AI Applications
Data scientists commonly struggle to effectively deliver their artificial intelligence (AI) models to customers. As a data scientist, in some cases, you might lack the software engineering ability to create a serving layer that exposes the model. You might also struggle with the operational part, by administering the infrastructe required to train and serve a model.
As any other piece of software, AI-based applications follow a lifecycle. If you do not have access to a consistent platform that allows you to move through this lifecycle, then your ability to deliver AI solutions can be seriously impacted.
As well as classic software engineering phases, such as deployment, or monitoring, AI systems bring additional requirements into their life cycle:
-
Teams must be capable to collect, store, read, verify, and preprocess data.
-
Then, they must have the ability to train data models by running multiple experiments, and be able to quickly reproduce those experiments.
-
They must also be able to serve a model, scale it up when necessary to meet the demands, or scale it down to save costly resources, such as GPUs.
-
Finally, the must be able to monitor the accuracy of the model in production, and detect any potential deviations from the expected accuracy and performance.
Red Hat OpenShift Data Science
Red Hat OpenShift Data Science (RHODS) is a platform that enables enterpises to train, build, deploy, and monitor AI-enabled applications. RHODS is the central piece of Red Hat OpenShift AI, a portfolio of products to cover the complete life cycle of AI applications, models, and workloads.
With RHODS, teams add a common platform to operate the complete lifecycle of AI-enabled applications:
-
Data scientists can start training their models on a common JupyterLab interface, which they are familiar with. They do not need to configure environments because their workbenches run on Red Hat OpenShift.
-
Software and Machine Learning Engineers can configure pipelines to integrate and deploy the models that result from Jupyter notebooks.
-
Cluster administrators can provide container images as customized working environments for data scientists, so that data scientists do not need to care about dependencies. They can also set quotas and scaling policies to optimize resource consumption.
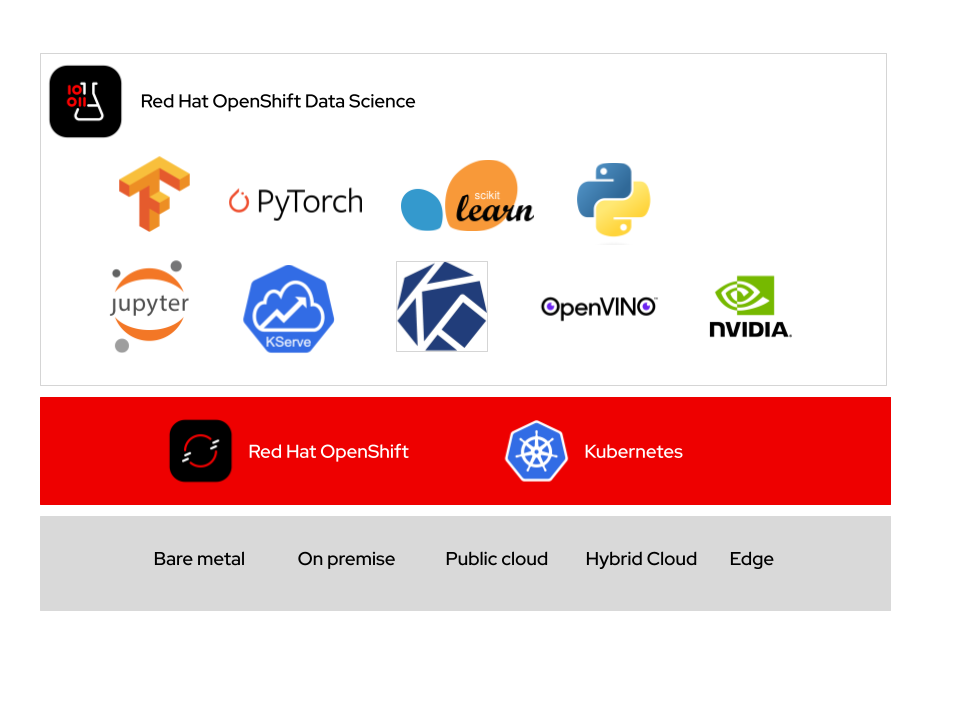
RHODS Architecture
RHODS is based on the Open Data Hub upstream project. Open Data Hub is an open source platform to handle AI lifecycles in hybrid clouds. It is based on Kubernetes, OpenSfhit, and operators.
RHODS incorporates the following elements:
-
Custom Jupyter-based environments on demand, called workbenches.
-
An set of curated and tested container workbench images, ready for data scientists to start working
-
Tested, certified, and supported integrations with the most popular AI technologies, such as Tensorflow, and PyTorch, among others.
-
Community-driven integrations, such as Airflow or mlflow.
-
A Model Serving framework to streamline model deployment and serving.
-
A UI console, integrated on OpenShift.
References
-
For more information, refer to the Getting Started with Red Hat OpenShift Data Science documentation at https://access.red hat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_openshift_data_science/1/html-single/getting_started_with_red_hat_openshift_data_science/index